Welding rod types and uses are critical knowledge for industrial buyers, distributors, and contractors who need predictable results across fabrication, maintenance, and repair projects. Understanding which rod to use in specific applications ensures stronger welds, reduced rework, and improved operational efficiency.
Industrial projects demand different rod characteristics depending on metal type, environmental conditions, and structural requirements. By providing comprehensive guidance and high-quality consumables, suppliers help professional buyers make confident, cost-effective choices.
Overview of welding rod types
There are several categories of welding rods, each designed for a particular purpose:
- Rutile-coated rods – Smooth arc and easy slag removal, ideal for general-purpose welding in workshops.
- Basic-coated rods – Low hydrogen, high strength, suited for structural welding and heavy-load applications.
- Cellulosic rods – Deep penetration, optimal for outdoor and pipeline work.
- Acid-coated rods – Smooth bead finish, suitable for specific projects with appearance-focused requirements.

Matching rod types to base metals
Correct rod selection depends on the base metal being welded:
- Carbon steel – Most common in industrial and construction applications.
- Low-alloy steel – Requires rods with controlled hydrogen content for structural integrity.
- Stainless steel or specialty metals – Use specialized rods designed for corrosion resistance and mechanical performance.
Professional guidance ensures that buyers select rods that minimize defects and improve weld longevity.
Performance considerations
Key performance factors include:
- Arc stability – Essential for consistent bead formation and reduced spatter.
- Mechanical properties – Tensile strength, elongation, and toughness must meet project standards.
- Heat control – Prevents burn-through, distortion, or weakening of the base material.
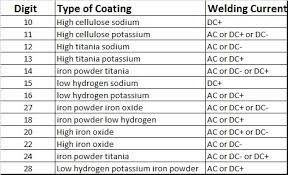
Practical applications for different welding rod types
Understanding welding rod types and uses allows buyers to align consumables with industrial needs:
- Structural fabrication – Use low-hydrogen or basic-coated rods.
- Equipment repair – Rutile-coated rods provide smooth, manageable welds.
- Outdoor pipelines – Cellulosic rods penetrate well in field conditions.
- Decorative-functional components – Acid-coated rods produce clean finishes.
Bulk supply advantages
Industrial buyers benefit from bulk procurement of multiple rod types. It reduces per-unit costs, ensures uninterrupted project timelines, and supports inventory planning for distributors and wholesalers.
OEM and ODM opportunities
OEM branding allows rods to be sold under the buyer’s own label, enhancing market recognition.
ODM customization enables adjustment of coating, packaging, or formulation to meet local requirements or specific industrial applications.
Safety and best practices
Fume control, proper ventilation, and protective equipment are essential. Suppliers providing clear guidance and technical support reduce operational risk and strengthen trust with professional buyers.
Long-term market relevance
Welding rod types and uses continue to be relevant across construction, industrial maintenance, agricultural equipment, and infrastructure projects worldwide.
Providing reliable consumables and technical guidance ensures consistent repeat business and positions your supply as a professional, B2B solution.
Final value proposition
Welding rod types and uses provide industrial buyers with practical solutions to achieve strong, consistent, and reliable welds. Supplying high-quality rods, guidance on selection, and OEM/ODM options strengthens operational efficiency, reduces defects, and positions your business as a trusted industrial partner.
